A microscope is an instrument used for different purposes usually in the science labs. The word ‘micro’ means micro-objects or very small elements and ‘scope’ means ‘to look’. Thus, the word ‘microscope’ means an instrument used to view or see the particles or objects which are not visible by the naked eye. It is used to discover the minor structures and do further observations on them. In this article you will get the detailed information about microscope parts and functions.
Table of Contents
Some Recommended Microscopes
Microscope Parts And Functions
The microscope is an important instrument of the science laboratories. Many research and studies are done using them. It plays a crucial role in studying the mechanism of small organisms and other objects. It has the ability to enlarge the minor objects which are not visible with the eyes i.e. you cannot see them without the help of a device.
It further produces the magnified images of these objects with definitive structures. This helps in getting the entire information about the various characteristics. Then, a detailed study is done on them to gather information.
Developed in the 16th century, this instrument has made several researching tasks easier for scientists and other people related to science. Many minute particles are present in the environment which are needed to analyze.
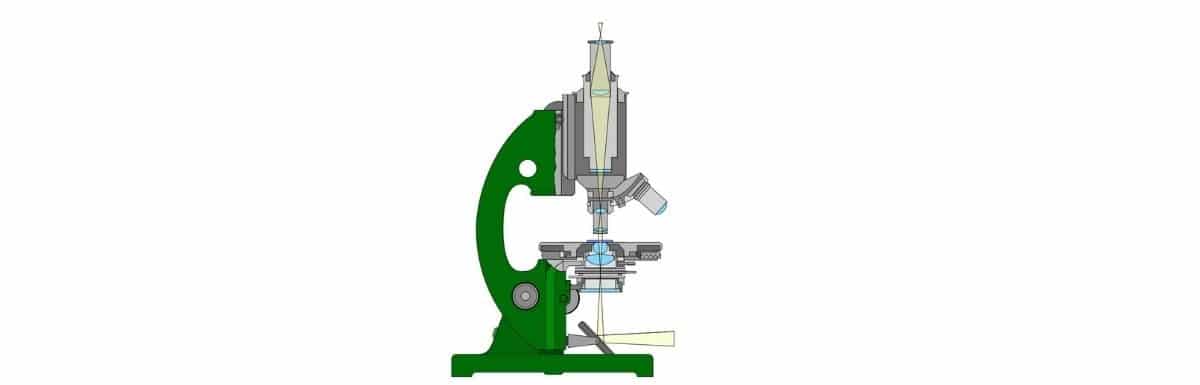
Parts of Microscope
The microscopes are made up of various lenses used for magnification purposes. These lenses have different magnification powers. On the basis of their focal strength, they are used to magnify the smaller objects. A microscope has different parts which have their own functions and contributes to getting better results. Here is the complete information about each part of the microscope:
1. Structural Parts Of A Microscope
• Head: Head is the structural part of the microscope. It is also known as the body of a microscope. It is responsible for providing support to the optical parts situated at the top part of the microscope.
• Base: It provides support to the microscope or the base on which the microscope stands. It also holds the illuminators of the microscope.
• Arms: This is an essential structural part of the microscope. It connects the base to the head. It connects the eyepiece tube to the bottom part of the microscope. It is further used for moving the instrument from one place to another. The advanced microscopes feature connected arms. They enable the better movement of the microscopic head. This ensures a clearer view of all the objects.
2. Optical Parts Of A Microscope
• Eyepiece lens: Eyepiece lens, also called an ocular lens, is the optical part used to view through the microscope. It is the first part visible in a microscope. The standard magnification is 10x. Also, there is an optional eyepiece providing the magnification ranging from 5x-30x.
• Eyepiece tube: This optical part is responsible for holding the eyepiece lens. It holds the eyepiece lens. The eyepiece tube varies for monocular microscopes and binocular microscopes. The tube of the former one is non-flexible whereas, for the latter, it is flexible and can be rotated to get the maximum visualization and adjusting the distance as well.
• Illuminator: It is a source of light used in place of the mirror. It reflects the light from the outside to the bottom of the microscope. It is situated at the bottom part of the microscope and reflects the light of low voltage of around 100v.
• Objective lenses: This is the main part of the microscope. These are the major lenses used for viewing the small specimens. You will find that there are almost 3-4 objective lenses in a microscope. These lenses either face towards the rare side or forward side of the microscope. The magnification powers of the lenses vary from 40x to 1000x such as 10x and 40x. In total, you can get the magnification of 1000x. For getting such good resolution, you have to buy a microscope with an Abbe condenser. You will find that the lens which is shorter in size is less powerful while the longest lens has the enormous power. The lenses with high-power are retractable i.e. protecting the lens and the slide by pushing at the end of the lens.
• Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: The revolving nosepiece of the microscope is also known as the turret. It holds and keeps the objective lenses at their position. It is rotatable to adjust the magnification power of the lens. It is movable and can be moved according to the power of the lens.
• Adjustment knobs: These knobs are essential for adjusting the focus of the microscope. In a microscope, there are two types of adjustment knobs, fine adjustment knob and the coarse adjustment knob. You can adjust the focus with these two knobs.
• Stage: This part is also crucial in studying an object. This is because on this part the specimen slide or object is placed for research. It is a flat surface on which the slides are positioned. There are stage clips on the stage used to clasp the specimen slide at its place and provide stability while doing the observation. Most of the microscopes have the mechanical stage and it helps to control the slides. It is done by adjusting the slides on the stage through mechanical knobs. There is no need to move them manually and can be done using the knobs on the stage.
• Abbe condenser: The abbe condenser is available with high-quality and powerful microscopes. This is designed for making the condenser movable and can provide the magnification of above 400x.
• Aperture: This is a hole in the stage of the microscope. Through this hole, the light enters the microscopic stage.
• Condenser lenses: The condenser lenses are used to take the light from the illuminator part to the specimen slide. They are located just below the stage and immediately after to the diaphragm of the microscope. They provide sharper and clearer images than the microscopes without these condenser lenses. They are used at the maximum power of 400x or above. The clarity of the image depends upon the magnification of the condenser lenses. A microscope with the power of 400x or above can receive great advantages with these condenser lenses. The lenses rated 0.65 NA or greater are considered as the best for this purpose. In case, the magnification power of the microscope is 1000x, then it is better to use the 1.25 Abbe condenser lens system. It can be moved in the upward and downward directions.
• Diaphragm: Diaphragm is also known as the iris of the microscope. It is situated just below the stage. The main role of this optical part is to control and provide the required amount of light to the stage of the microscope. It is adjustable and therefore it is possible to regulate the power and the quantity of the light beam that is focused on the specimen. It is done through the various holes of the diaphragm. The high-power microscopes include the diaphragm with an Abbe condenser. They collectively control the focus of the light reaching the specimen.
• Rack stop: It restricts the distance between the objective lens and slide and maintains an accurate space between them. It makes sure that the specimen slide doesn’t get too close to the objective lens and prevent it from damage. In other words, it controls that the slide doesn’t come too far up that it hit the objective lens. However, it is not required in each situation and used only for very thin slides. In case, you are not able to look the slide at the maximum magnification power, then it is also useful in that situation.
• Condenser focus knob: This knob is responsible for moving the condenser up and down. It maintains the light that reaches the stage where the specimen slide is present.
Functions of a Microscope
The microscope is an important instrument for both biology and chemistry experiments. It is used for different purposes and provides better magnifying results. The various microscopes are available providing different levels of magnifications. This helps in generating images of distinct qualities. Even some microscopes have the potential to look at the atoms also. There are a few types of microscopes available that provide different quality of results and have various functions:
1. Compound Microscopes
The compound microscope is the most common form of optical microscope used in the science laboratories. It makes use of different lenses to provide improved magnification. It has four lenses, of which one is viewing lens that magnifies the objects 10 times while other lenses magnify an object 10, 40, and 100 times. However, the images produced by this microscope is of lower resolution than the images produced by other microscopes. These microscopes are used to study the plant cells and also for evaluating the various animal cells and bacteria as well.
2. Stereo or Dissection Microscopes
The stereo microscope or dissection microscope is used to produce three-dimensional images of the specimen. It makes use of the two different viewing lenses to produce the image. This microscope, however, doesn’t have the potential to magnify the images more than 100 times. It is not as powerful as compared to the compound microscope. They generally produce the images at the magnification power of below 100x. They are used for microsurgeries, developing watches, and creating circuit boards.
3. Imaging Microscopes
Imaging Microscopes are more advanced and powerful than optical microscopes. The high-resolution and better magnification are the features available with the imaging microscopes. They make use of the beams containing radiations or particles that create the image.
The functions of a microscope depend upon the parts of a microscope. It means that the parts of the microscope are responsible for performing each and every function. You have already got the information about the different parts of a microscope and here are the details about their functions:
• Head and Base: The head and base part of the microscope forms the outer structure. They support the entire microscope and provides the base to it. The head part supports the upper portion of the optical parts. On the base part, the microscope stands and provides stability during the research works.
• Arms: The arm part of the microscope has several functions. First of all, it connects the head of the device to the base. It also helps in carrying the microscope from one location to another.
• Eyepiece lens: The eyepiece lens, also known as an ocular lens, is used for seeing through the microscope. The power of the lenses varies from 10x to 15x. The multiplication of the magnification gives the total level of magnification. It forms a sharp image and is clearly visible. It further magnifies the intermediate image for a clear view of the specimen. The eyepiece tube holds the eyepiece at its position and provides stability to it.
• Illuminator: The illuminator is responsible for providing a constant light to the specimen slide. The light microscopes use the low voltage and halogen bulbs with continuous lighting control.
• Stage: The stage is the part where the specimen slide is placed. It ensures that the slide remains at its place and provide better results while researching. The mechanical stage is also available with some of the microscopes. It helps in controlling the slide and there is no need to adjust it manually.
• Objective lenses: The objective lenses are an essential part of a microscope. They collect the light from the specimen and produces the real and focused image on the ocular lens. They are responsible for primary image formation, determining the quality of the image produced, and maintaining the level of magnification and resolution. The lenses with high-power are retractable i.e. protecting the lens and the slide by pushing at the end of the lens.
• Revolving Nosepiece: It is responsible for holding the different lenses. It can be adjusted to achieve various levels of magnification. Due to the revolving nosepiece, a microscope has different magnification levels.
• Adjustment knobs: These knobs are used for adjusting the focus of the microscope.
• Condenser lenses: The condenser lens performs the function of bringing the light from the illuminator part and then focuses it towards the specimen slide. They ensure to provide clear and sharp images. The magnification power of the condenser lens decides the quality of image, i.e. high-power condenser lens provides a clear and focused image.
• Diaphragm: Diaphragm, also known as iris, is responsible for regulating the amount of light reaching the slide. It is easy to use and is flexible also. This means that you can easily control the intensity and size of the beam of the light focused towards the slide.
• Rack stop: It plays an essential function while using the microscope. It maintains the distance between the slide and the objective lens. It prevents the slide from coming too close to the lens and helps in protecting it from any kind of damage. You can adjust the distance and get a clear view of the specimen.
Microscope performs various functions and is an essential instrument of the science labs. Medical science makes use of this instrument to study different aspects of an organism and its cells. Studies on tissues and cells are conducted through a microscope. They are then analyzed to gather the information and the changes which are occurring in them.
For scientists, a microscope is a significant device to research the various proteins present within the cells. Even some microscopes have the potential to look at the atoms and conduct the study about the atomic structures. The electron microscopes are also used to perform functions such as creating the small electrical circuits. These microscopes use an electric beam that is reflected in the specimen. They are also used to examine cells and microorganisms.
The function of the parts of a microscope varies and it is better to understand them in order to use the microscope properly. They are adjusted according to the viewer’s needs and the object on which he/she is working. The magnification capacity also depends on the type of microscope. Also, there are many uses for which it is used. Most of the activities of the laboratories are conducted with the help of a microscope.
How to Focus or Use the Microscope
Step 1
In the first step, you have to prepare the specimen slide you want to study. First of all, you have to place a coverslip over the specimen sample. This is important to do this step before using the microscope. The sample is flattened with the coverslip to provide a clear image. Also, the coverslip contains the fluid within the flattened slide.
Step 2
Now, you have to begin using the microscope. Initially, you have to start with the 4x objective lens i.e. with the lowest magnification level. It is better to start with a low level and then proceed towards the maximum levels. You can adjust it through the revolving nosepiece of the microscope. This helps in getting a proper focus on the sample. It prevents the slide from breakage due to the objective lens and maintains an accurate distance between them. Then, you can move to the next level of magnification power. After ending the process, you can reset it to the initial low level.
Step 3
You should always remember to not to put pressure while focusing on the microscope. You can look at the objective lens and the stage to ensure that they are correctly adjusted. Don’t forget to turn the focus knob and adjust the stage. Now, view through the eyepiece and rotate the knob until the image gets appeared.
Step 4
In this step, you have to adjust the illuminator for getting the proper amount of light. You need to use the adjusting knobs and condenser lens for getting a sharp and clear image.
Step 5
When you receive the proper image at the lowest level of magnification, you can change the magnification of the objective lenses. You can adjust the sample or the amount of light according to the requirements. After studying the slide, you have to lower the stage and remove the slide.
Final Thought
The microscope is one of the instruments which is available in all of the science labs. It is used to view the small microorganisms or other objects not visible with the naked eyes. You need learn about microscope parts and functions to help accomplish different scientific tasks. Along with proper usage proper maintenance is also required while using a microscope.
This device is not difficult to use but requires the knowledge of different parts before using it. The entire details about the parts and their functions are provided in this article and you can gather the required information. As now you have lot of knowledge about microscope we should also check out the history of the microscope.
Bopha Rightwell says
It is a good article. I have like it.